之前和大家提過, 如何檢查 Scrum 執行深不深入. 結果馬上就有人接著問說那 Kanban 呢? 是不是也有雷同的檢查方式? 沒錯, 讓我們來瞧瞧.
David Anderson 在 London Lean Kanban Day or Agile China in 2013 中有個演講: Deep Kanban - Worth the Investment?, 他提到了如何衡量你看板方法實施的深度如何.
http://www.djaa.com/sites/ltdwip/DepthOfKanban.pdf
他分成了六個面向來討論:
1. 視覺化
只列出工作項目
不同工作項目的類別
有描述工作流程
Kanban Limits
有 ready for pull 的欄位
Blocking issues
產能分配 (Capacity Allocation)
度量相關的指標 (lead time, local cycle time, SLA)
不同工作項目間的關聯性
不同工作流程的關聯性
Risk dimension (cost of delay, tech risk, market risk)
2. 限制同時工作的數量
沒有限制 WIP (Last Responsible Moment)
Proto-Kanban
personal kanban
針對個人限制 WIP limit
對於 done 欄位沒有限制 WIP limit
單一的工作流程, 裏面全部設定了 WIP limit, 並且使用拉式觀念
多個有關聯的工作流程, 並且使用拉式觀念
3. 管理流程
每日立會
累積流程圖 (Cumulative Flow Diagram)
Delivery rate (velocity/throughput) control chart
SLA or lead time
flexible staff allocation or swarming behavior
deferred pull decisions, or dynamic prioritization
有關於流程評估的度量(number of days blocked, lead time efficiency)
4. 明確的政策
針對工作流程/Kanban 訂定政策
pull criteria (做完的定義, 離開的條件)
產能分配 (Capacity Allocation) 的政策
queue replenishment (指如何選擇接下來要做的事情)
針對不同服務等級 (class of service) 的政策
針對人員配置/工作指派的政策
5. 回饋的迴路
週期性在工作版前面舉行團隊的會議 (通常是每天)
Coaching Kata
Operations Review
6. 改進
局部流程的改進 - 針對工作流程, 政策, 和 WIP limit
增進 Kanban 實踐的深度 - 針對上述 5 個面向
Evidence that process evolution was model-driven-use of metrics, identification of bottlenecks, common/special cause variation, transaction/coordination costs, other models not specified in current literature
Evidence of process or management policy evolution as a result of mentor-mentee relationship
Evidence of inter-workflow process or management policy evolution as a result of operations review
如果用雷達圖來表示的話, 可以長得像這個樣子:
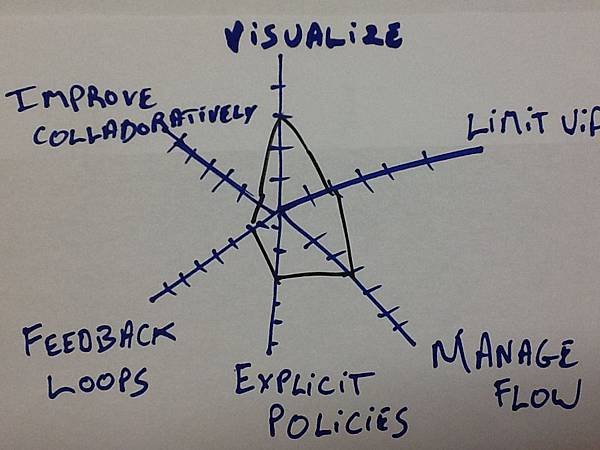
David Anderson 說 kanban 沒有所謂執行的好不好, 但有所謂的深入不深入. 實施的淺, 也是可以得到不少好處, 並且可以鼓勵他們開始採用 Kanban.
但是對我來說, 它算是一個很棒的檢查清單, 讓你知道有哪些項目你還不知道. 我真的發現有好多項目我完全不懂, 我想今年有好多東西需要看了.
不過發現我在 scrum 和 kanban 兩邊的評量表, 得分都很低耶, 代表我沒做到的還真多 ....
註1: 之前提到的 Proto-Kanban 大概會長得像這樣
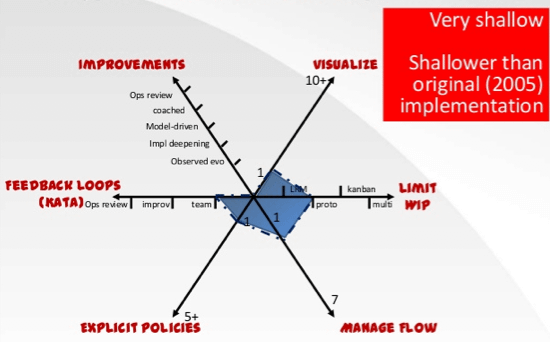
註2: 藍色的那些項目, 都是我不了解的. 所以不知要怎麼翻才比較合適, 因此保留原文


 留言列表
留言列表

